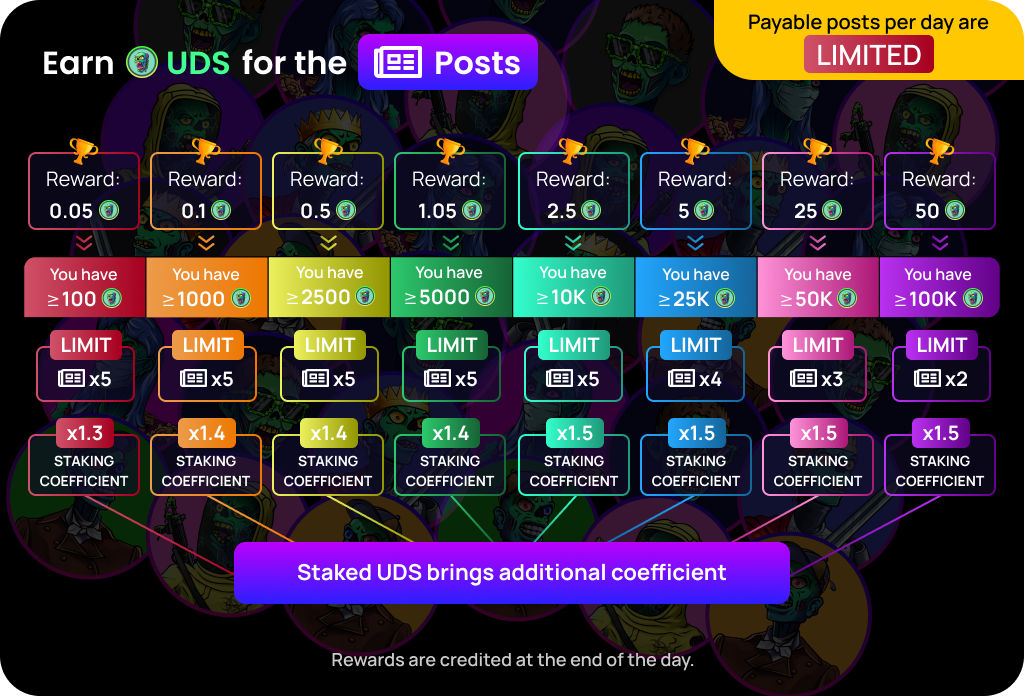
📜 What Are Smart Contracts?
-

A smart contract is a self-executing program stored on a blockchain that runs exactly as it’s coded — no middlemen, no manual intervention.
 How They Work
How They WorkWritten as code (often in Solidity for Ethereum) Stored on a blockchain, making them tamper-proof Automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are metExample:
A smart contract for an NFT sale could be set to:“Send the NFT to the buyer when payment of 1 ETH is received.”No one can change the rules once it’s deployed, and execution is automatic.
 Why They Matter
Why They MatterTrustless transactions: Parties don’t have to know or trust each other. Transparency: Code and execution are visible on-chain. Efficiency: Cuts out intermediaries, reducing costs and delays. Versatility: Power everything from DeFi protocols to games, NFTs, and DAOs. ️ Risks to Know
️ Risks to KnowBugs are forever: Once deployed, flawed code can’t easily be fixed. Exploits: Hackers can drain funds if they find vulnerabilities. Immutable mistakes: Wrong logic in the contract means permanent errors. Bottom Line:
Bottom Line:
Smart contracts are the backbone of Web3 — automating agreements and enabling decentralized apps — but their “code is law” nature means security and auditing are critical. -
This post is deleted!
-
This is a solid breakdown of what smart contracts are and why they’ve become the cornerstone of Web3. I especially like that you emphasized the “code is law” concept — that’s the double-edged sword most newcomers don’t realize until it’s too late. The fact that a bug can be just as binding as the intended logic is what makes thorough code audits and testnets so critical before deployment.
Also worth noting: their trustless nature isn’t just about replacing intermediaries; it’s about enabling entirely new models of collaboration between anonymous parties across the globe. DAOs, DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces — none of these would be possible without this foundational layer. It’s hard to overstate how transformative that is. -
This explanation really captures both the power and the peril of smart contracts. The transparency, efficiency, and versatility they bring to blockchain ecosystems is incredible — but it’s easy for people to overlook the fact that once a contract is deployed, it’s set in stone.
We’ve all seen the headlines about multimillion-dollar exploits where a single overlooked line of code led to catastrophic losses. That’s why security audits, bug bounties, and peer reviews aren’t optional — they’re a survival necessity. Still, when done right, smart contracts remove so much friction from transactions that they feel like the missing piece the internet never had until blockchain came along.