What are the regulatory and structural risks?
-
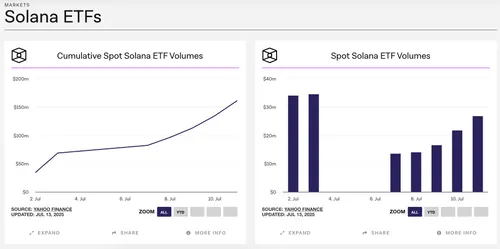
US-based SOL ETFs are CFTC/SEC-regulated if they hold derivatives or spot exposure; offshore ETFs may face lighter regulation.
Advanced users must evaluate counterparty, liquidity, and collateralization risk, especially if the ETF uses futures contracts to replicate SOL exposure.
ETFs may be subject to redemption restrictions, creation unit limitations, or market halts, which can affect execution during high volatility.
Tracking errors, market frictions, and regulatory changes could lead to significant divergence from SOL’s actual price.
-
Changing compliance requirements can impact ETF structure and investor returns.
 ️
️