🚨 Largest Supply Chain Hack in History Targets JavaScript Libraries — Crypto Users at Risk
-
Hackers have compromised widely used JavaScript libraries in what experts are calling the largest supply chain attack ever recorded, injecting malware designed to steal crypto by swapping wallet addresses and intercepting transactions.
 How the Hack Happened
How the Hack HappenedAttackers gained access to a reputable developer’s NPM (Node Package Manager) account through phishing emails disguised as official support.
Once inside, they added malicious code to popular packages such as chalk, strip-ansi, and color-convert.
These libraries, downloaded over 1 billion times per week, are buried deep in countless app dependency trees — meaning even devs who never installed them directly may be exposed.
🪤 What the Malware Does
The injected code acts as a crypto-clipper:
It silently replaces wallet addresses during transactions.
Users relying only on software wallets are most vulnerable.
Hardware wallet users are protected, since they must confirm the final details on a physical device.
Ledger CTO Charles Guillemet warned:
“The affected packages have already been downloaded over 1 billion times, meaning the entire JavaScript ecosystem may be at risk.”
 ️ What Users Should Do
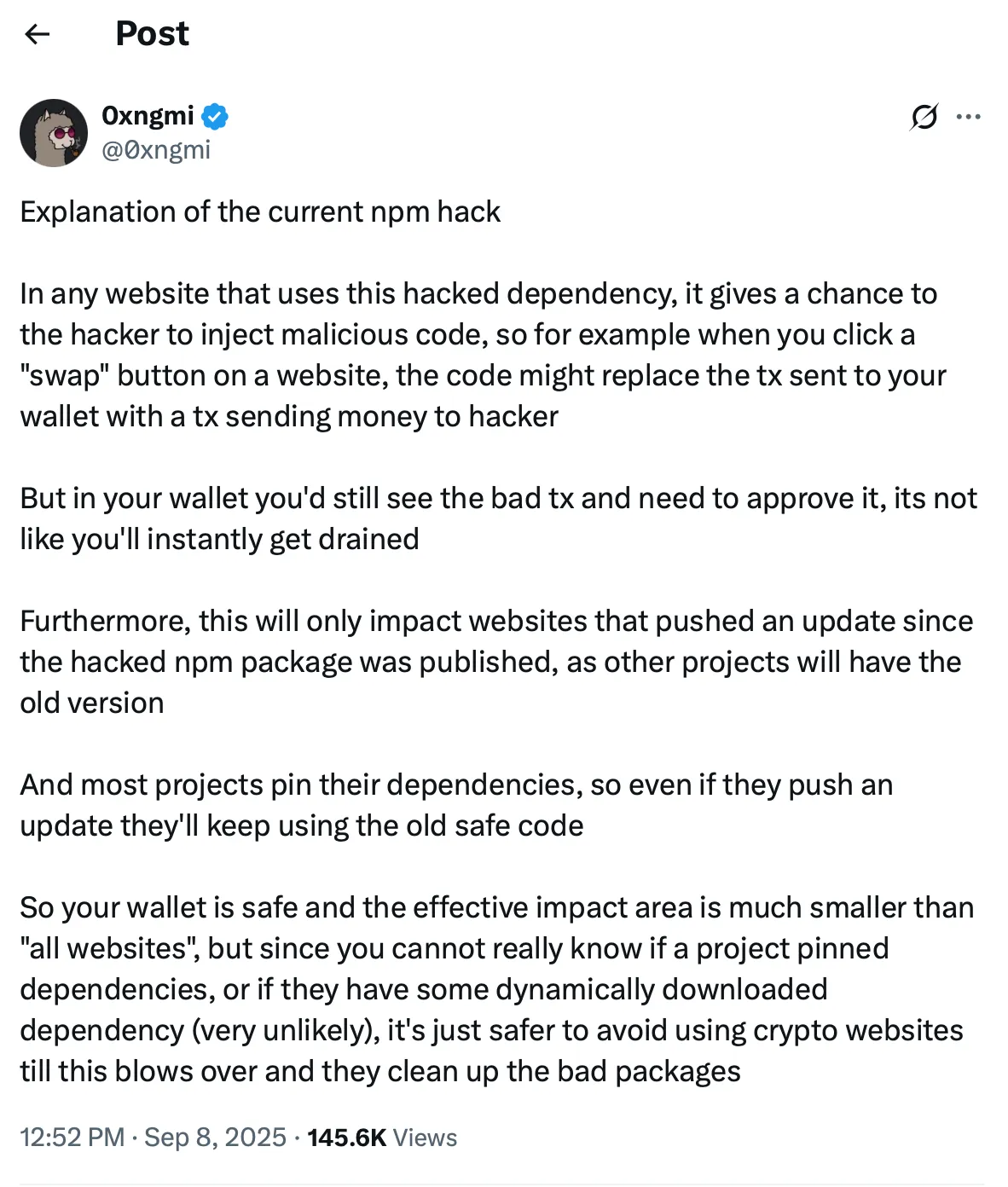
️ What Users Should DoAccording to DefiLlama founder Oxngmi, the malware won’t auto-drain wallets — but if you hit “swap” or approve a transaction on an affected site, it may redirect funds.
Only projects updated after the malicious code was published are at risk, but since users can’t easily check which sites are safe, security experts recommend avoiding crypto transactions until fixes are deployed.
🧑
 Why It’s So Dangerous
Why It’s So DangerousThis hack goes far beyond simple code injection:
It can alter website content,
Tamper with API calls, and
Manipulate what apps display to users before they sign a transaction.
Security researcher Charlie Eriksen noted:
“The attack operated at multiple layers, making it one of the most dangerous supply chain compromises we’ve ever seen.”
 Takeaway: If you’re moving funds, use a hardware wallet and double-check every transaction detail. For now, treat most web-based crypto apps with extra caution until developers confirm they’ve cleaned their dependencies.
Takeaway: If you’re moving funds, use a hardware wallet and double-check every transaction detail. For now, treat most web-based crypto apps with extra caution until developers confirm they’ve cleaned their dependencies.