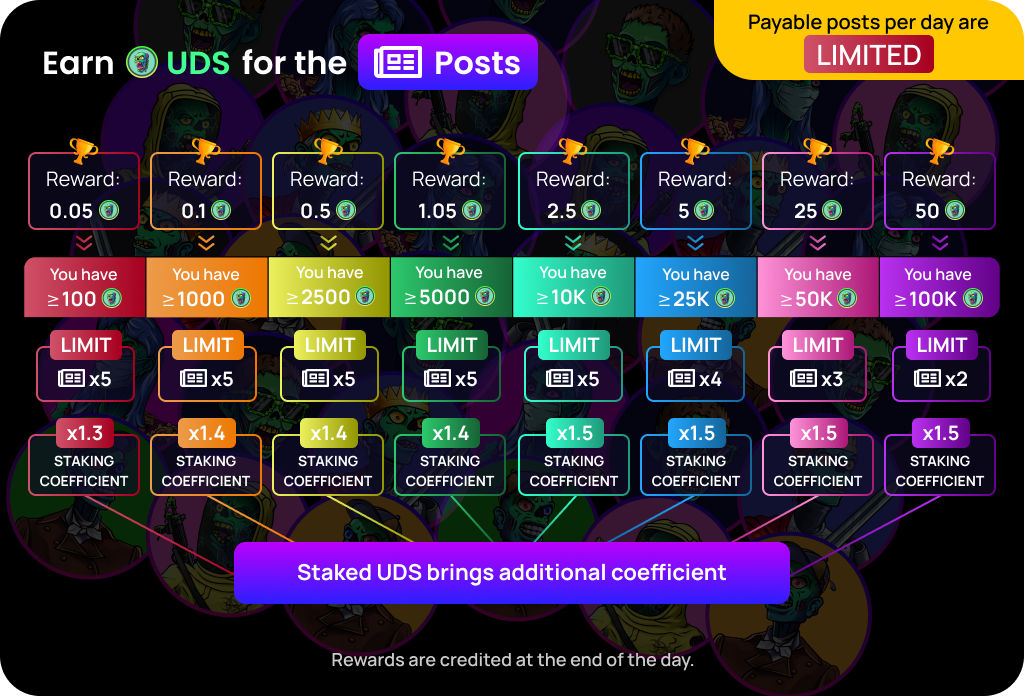
Trade and Its Impact on Economics
-
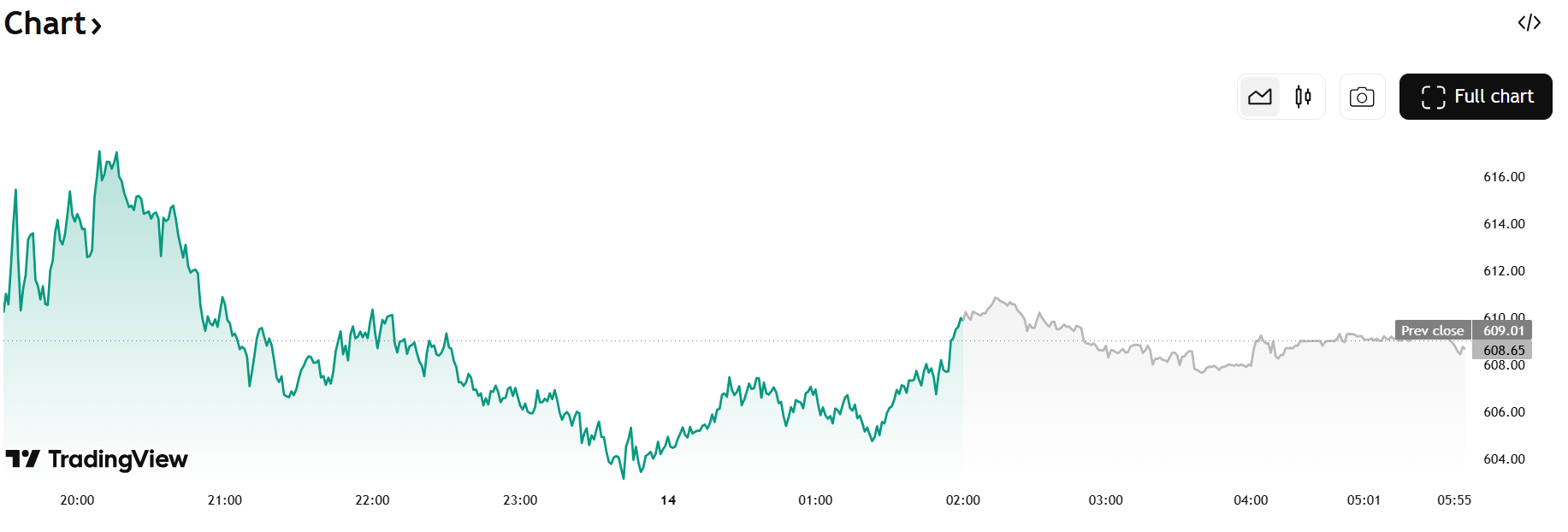 1. The Fundamentals of How Trade Affects Economics
1. The Fundamentals of How Trade Affects EconomicsTrade affects economic performance through the principles of comparative advantage, resource specialization, and market efficiency. Nations produce goods for which they are most efficient and trade them for goods that others produce more efficiently. This specialization boosts productivity, lowers costs, and expands consumer choices.
Trade influences economics through multiple channels:
a. GDP Growth
Exports contribute directly to a country’s gross domestic product (GDP). The more a nation exports high-value products, the faster its economy tends to grow. Weekly export orders, new shipping data, and port activity often give early signs of GDP trends.
b. Employment and Industrial Development
Trade expands industries that are competitive internationally. For example, countries with strong textile or automobile sectors benefit from higher employment, foreign investment, and supply-chain expansion. At the same time, weaker industries may contract if they cannot compete globally.
c. Consumer Welfare
Trade reduces prices, increases product variety, and improves quality due to global competition. Weekly changes in import costs—such as falling crude oil prices—can reduce inflation pressure in importing nations.
d. Technological Transfer and Innovation
Countries gain access to foreign technologies and advanced machinery via trade. Regular shifts in semiconductor, electronics, and machinery trade flows can influence domestic productivity.
e. Currency Strength and Balance of Payments
International trade impacts a nation’s currency value. A trade surplus strengthens the currency; a deficit weakens it. Weekly foreign exchange movements are closely tied to changes in import and export demand.
- Weekly Dynamics: What Drives International Trade Movements?
Weekly trade analysis observes short-term shifts that affect long-term economic trends. Several global factors influence trade every week:
a. Commodity Price Movements
Prices of crude oil, gold, natural gas, and agricultural goods often fluctuate weekly.
Oil-importing countries benefit when crude prices fall, reducing inflation and supporting growth.
Commodity-exporting countries—such as Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and Australia—see weekly revenue changes due to price volatility.
b. Currency Exchange Rate Movements
A stronger domestic currency makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive.
For instance, if the Indian Rupee strengthens against the USD in a particular week, India may see cheaper imports of crude oil, electronics, and commodities.c. Supply Chain Disruptions
Events such as port congestion, strikes, storms, or geopolitical tensions can cause weekly disruptions that affect global trade routes. The Red Sea, Suez Canal, and Taiwan Strait are common areas where disruptions impact trade flow.
d. Trade Policies and Government Announcements
Tariff changes, export restrictions, and free-trade agreements directly affect trade. Weekly policy updates from the US, EU, China, and India often move global markets.
e. Global Demand Cycles
A weekly slowdown in retail sales or industrial production in major economies—such as the US, China, Europe—can reduce demand for imports, influencing global prices and shipment volumes.
- Weekly International Trade Analysis: What Typically Happens in a Week?
A weekly trade overview helps understand real-time economic conditions. Here's how international trade patterns typically evolve in a week:
a. Export and Import Data Releases
Many countries release weekly trade metrics, including:
cargo volumes
port container movements
shipping freight rates
export order books
commodity inventory levels
These indicators show which industries are expanding or slowing.
b. Shipping and Logistics Trends
Weekly changes in:
freight charges
vessel availability
port turnaround time
affect trade costs. High freight rates usually slow trade; low rates encourage more shipments.
c. Commodity Market Volatility
Global commodity exchanges like NYMEX, LME, and ICE influence trade flows weekly.
For example:A rise in metal prices boosts export revenue for miners.
A fall in food grain prices affects agricultural exporters.
d. Supply and Demand Imbalances
Each week, new data about crop yields, factory output, or consumer demand shifts global trade flows. If China announces weak factory activity, metal and energy shipments fall globally.
e. Global Trade Sentiment
Market participants watch weekly events like:
central bank speeches
geopolitical developments
economic data releases
These influence the willingness to trade and invest across borders.
- Impact on Emerging and Developed Economies
Trade affects economies differently depending on their industrial structure, currency position, and dependence on imports.
a. Developed Economies
Countries such as the US, Germany, and Japan rely on:
high-value exports (technology, automobiles)
stable supply chains
diversified trade partners
Weekly trade data in these nations signals global economic direction.
b. Emerging Economies
Countries like India, Brazil, Indonesia, and Vietnam are more sensitive to:
commodity price shifts
currency fluctuations
changes in global consumption
Weekly export performance in textiles, chemicals, IT services, and agriculture significantly shapes economic conditions.
c. Least Developed Economies
These countries rely heavily on a few products (mining, agriculture). Weekly price shifts in commodities can greatly affect national revenue.
- Trade Challenges Observed in Weekly Trends
a. Protectionism
Increasing tariffs and export controls from major economies create weekly uncertainty.
b. Geopolitical Tensions
Conflicts and sanctions disrupt weekly trade flows, affecting currencies and commodity prices.
c. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Still recovering from the pandemic, global logistics systems remain fragile.
d. Inflation and Cost Pressures
Rising freight costs or supply shortages can lead to weekly price fluctuations internationally.
- Conclusion: Why Weekly Trade Analysis Matters for Economics
International trade is a dynamic system that directly influences global economic health. Weekly fluctuations in shipping rates, commodity prices, policy announcements, and currency movements have both short-term and long-term impacts on national economies. These weekly movements help analysts forecast inflation, GDP growth, and investment sentiment.
Understanding these patterns is essential for:
investors
businesses
policymakers
traders
economic researchers
In an interconnected world, weekly international trade developments provide early, real-time insights into economic direction, making trade one of the most critical components of modern economic analysis.
-
Trade policies shape long-term economic growth more than most people realize.
-
Trade expands industries that are competitive internationally. For example, countries with strong textile or automobile sectors benefit from higher employment, foreign investment, and supply-chain expansion. At the same time, weaker industries may contract if they cannot compete globally.